The Neptune Project
Almost 2 million children in America ages 0-6 have unsafe lead levels.
Lead poisoning leads to irreversible brain damage in youth, an is entirely preventable.
I used a two-pronged approach to make testing more efficient:
Use machine learning to predict areas most at risk for lead contamination
Develop a “litmus test” to easily and affordably detect unsafe lead levels
Machine Learning Model
Collecting BLL data of children is mandated in my home state, California. Using this publicly available dataset, I trained a model to predict lead hotspots based on a variety of factors that I gathered from the US census.
Since census data is available for all 50 states, the model determined by training census data on CA BLL data allows us to predict the BLL levels of zip codes in any other state that don’t have universal access to testing.
Census data used to predict where lead hotspots are.
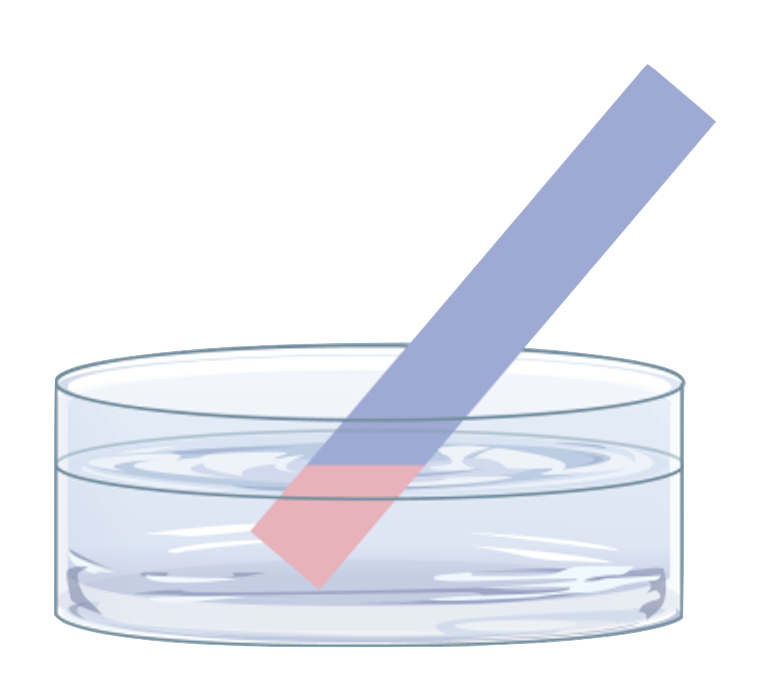
Turns purple to indicate unsafe amount of lead.
The test uses a chemical called sodium rhodizonate which reacts with aqueous lead ions to form the purple color.
Litmus Test
Prototyping in 2017
Prototyping in 2020